Digestive System Review Guide Answers
Chapter 15: Study Guide Original Document: 1. What is peristalsis? muscular movements that push food through the alimentary canal 2. What are papillae and where are they located? taste buds, tongue 3.
What is the roof of the oral cavity called (2 parts): soft and hard palate Where is the uvula? Back of the mouth, throat area 4.
What are the three salivary glands and where are they located? Parotid (ear), submandibular (below jaw), sublingual (below tongue) 5. What are the two types of movements within the alimentary canal? mixing and propulsion 6. What are the three main functions of the digestive system?
1) mechanical and chemical break down of food 2) absorption of nutrients 3) elimination of wastes 7. What is the name of the opening where the esophagus pass through the diaphragm?
esophageal hiatus 8. What layer of the alimentary canal carries out absorption? Mucosa What layer contains glands, blood vessels, and nerves?
Submucosa What layer contains the muscles? Muscular What layer covers the structures? What valve opens from the esophagus to the stomach?
Cardiac sphincter What valve opens from the stomach to the small intestine? Pyloric sphincter 10. What structure connects the tongue to the floor of the mouth? What digestive enzyme is produced by the salivary glands?
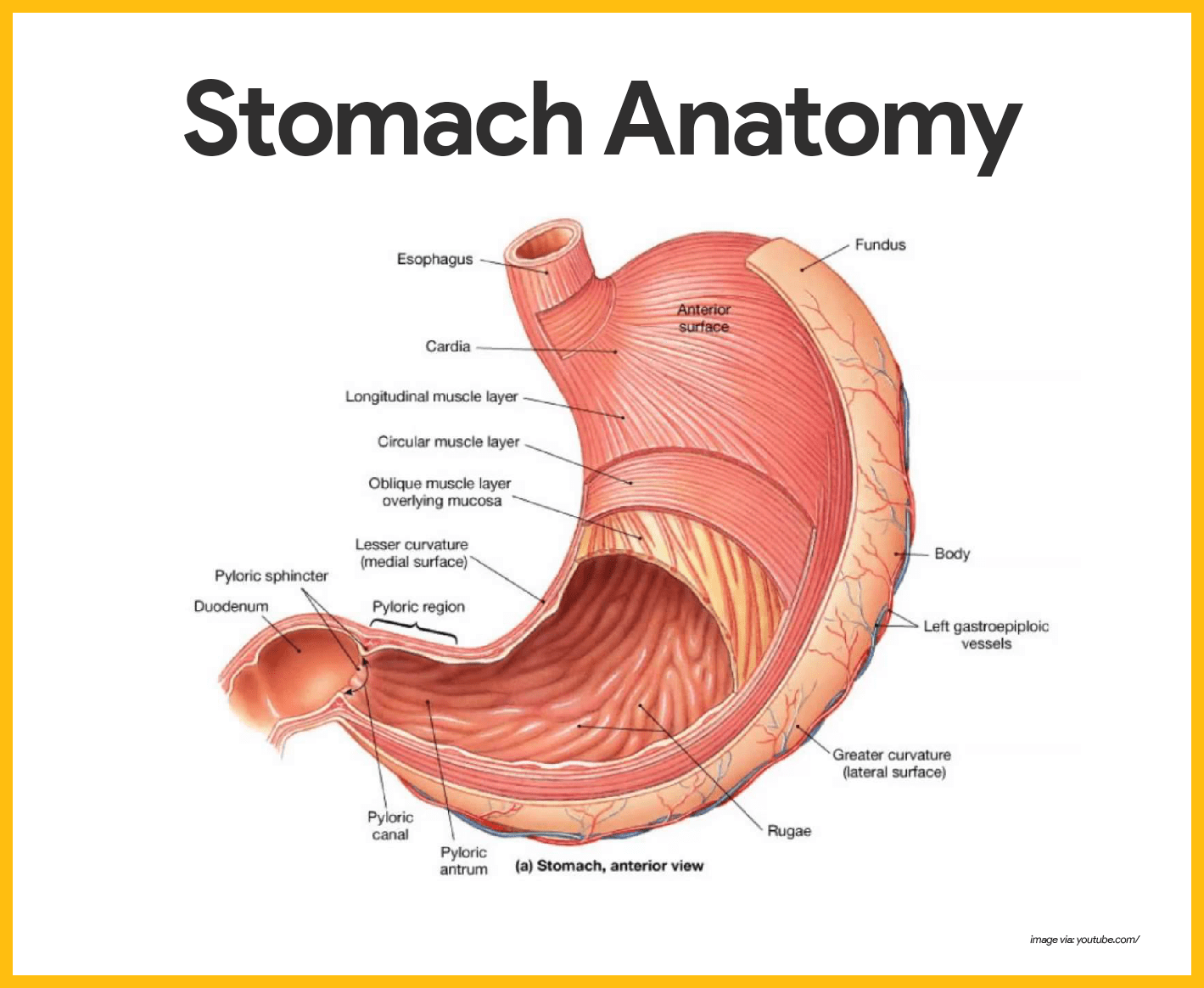
The part of the stomach that sits slightly above the esophagus is called the fundus 13. What is the hardest substance found in the body? Tooth enamel 14. The central cavity of the tooth is made of dentin The top of the tooth is called the crown The part of the tooth that extends below the gums is called the root 15. The front teeth are called incisors. The back teeth are called molars The pointed teeth after the incisors are the canines or cuspids 16. What is food called after it has been broken down into a paste?
Chyme What are the folds inside the stomach called? What causes jaundice in newborns? Liver is not functioning 18. Trace the path of food once it enters the colon (follow through the parts) ascending colon to transverse colon to descending colon 19. What is the function of the pancreas?
Digest foods 20. What does the bile duct connect? gall bladder to the duodenum 21. Where is the hepatic portal vein located?
The liver 22. Trace the path of food from the stomach and through all of the parts of the small intestine: stomach: duodenum jejunum ileum. Which section is the longest? What is the function of the gall bladder?
Store bile What is the function of bile? Digest fats 24. What membrane holds the coils of the small intestine together? mesentery What membrane covers the organs of the digestive system like a curtain? greater omentum 25.
What is the function of the intestinal villi? Increase surface area for absorption 26. What part of the colon is located right before the rectum? sigmoid colon 27.
Where is the cecum located? At the junction between the small intestine and the large intestine What “useless” structure is attached to it?
What part of the system stores waste prior to its elimination? What is a mass movement? Defecation, elimination of solid waste.
The “flora” of the large intestine is what? What is the function of the large intestine? Reabsorption of water if this function does not work, what sickness can result?
Dysentery or diarrhea 32. If part of the small intestine pokes through the abdominal muscles, a person has a hernia 33. Hepatitis (A,B, or C) affects which organ of the digestive system? The majority of a human’s diet should consist of what? Grains, vegetables 35.
What substance is mainly responsible for breaking down fats? Bile What substance is created in the stomach and breaks down food? What is lactose intolerance? Inability to break down milk (lactose) 37. What is another name for gastroesophageal reflux disease? Acid reflux 38. The biliary system refers to the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
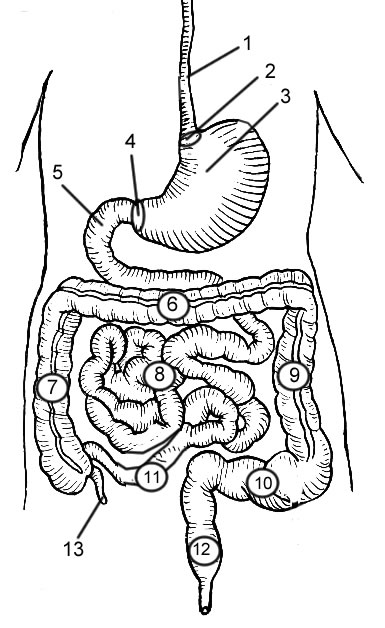
What are the three ducts found in that system? Hepatic, cystic, common bile 39. If a person has dysentery, they have a dangerous form of diarrhea 40. Be able to label structures of the digestive system on an image.
The Asphalt Institute (AI) and the Asphalt Emulsion Manufacturers Association (AEMA) are pleased to offer the 4th edition of MS-19, The Basic Asphalt Emulsion. Asphalt institute manual series 19.
(This includes a close-up view of the stomach and biliary system).
Chapter 14 Digestive System Study Guide Answers
. The digestive tract (alimentary canal) is a continuous tube with two openings: the mouth and the anus. It includes the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Food passing through the internal cavity, or lumen, of the digestive tract does not technically enter the body until it is absorbed through the walls of the digestive tract and passes into blood or lymphatic vessels. Accessory organs include the teeth and tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. The treatment of food in the digestive system involves the following seven processes:. Ingestion is the process of eating.
Propulsion is the movement of food along the digestive tract. The major means of propulsion is peristalsis, a series of alternating contractions and relaxations of smooth muscle that lines the walls of the digestive organs and that forces food to move forward. Secretion of digestive enzymes and other substances liquefies, adjusts the pH of, and chemically breaks down the food. Mechanical digestion is the process of physically breaking down food into smaller pieces.
This process begins with the chewing of food and continues with the muscular churning of the stomach. Additional churning occurs in the small intestine through muscular constriction of the intestinal wall. This process, called segmentation, is similar to peristalsis, except that the rhythmic timing of the muscle constrictions forces the food backward and forward rather than forward only. Chemical digestion is the process of chemically breaking down food into simpler molecules.
The process is carried out by enzymes in the stomach and small intestines. Absorption is the movement of molecules (by passive diffusion or active transport) from the digestive tract to adjacent blood and lymphatic vessels. Absorption is the entrance of the digested food (now called nutrients) into the body. Defecation is the process of eliminating undigested material through the anus.
Recent Posts
- Manual Of Leaf Architecture
- User Manual For Seat Ibiza 2016
- Simple Comfort 2001 Thermostat Manual
- 1993 Buick Regal Service Manual
- 2005 Mustang Service Manual
- 2015 Ccna Study Guide 200 120
- Honda Ct 125 Workshop Manual
- Peachtree Study Guide Answers
- Thomas Skid Steer 1 33 Repair Manual
- 2002 Vw Gti Service Manual
- Toyota Hilux Service Repair Manual 1989 2017
- Solution Manual For Introductory Statistical Mechanics Bowley
- Renault Scenic Ii Repair Manual 2001
- Kubota Bx1860 Mower Owners Manual
- 2015 Lt50 Service Manual
- Qca Maths Year 3 2015 Teacher Guide





